February 20, 2026
10 Best Knowledge Management Practices to Scale Your Business in 2026
Discover the top 10 best knowledge management practices to improve efficiency and scale your teams. Actionable tips for agencies, support, and ops.
In a world of distributed teams and complex workflows, 'tribal knowledge' isn't just inefficient; it's a critical business risk. When essential processes live only in the minds of a few key employees, your agency, support team, or SMB is constantly one resignation away from operational chaos. The solution lies in building a robust, living knowledge system. This system must not only capture what your team knows but make that information accessible, actionable, and simple to maintain.
This article moves beyond generic advice to detail the 10 best knowledge management practices that modern, high-performing teams are using to standardize operations, onboard new hires faster, and scale with confidence. We'll explore specific, actionable strategies tailored for the unique challenges faced by:
Agencies and consultants delivering SOPs to clients.
Customer success and support teams documenting product workflows.
Operations and HR managers standardizing onboarding processes.
SaaS and product teams creating customer-facing guides.
Distributed teams and SMBs seeking scalable process documentation.
Forget the outdated, static wiki. We will cover everything from visual process documentation and interactive guides to engagement analytics and continuous improvement workflows. You'll learn how to implement these practices to transform scattered documents and endless Slack threads into a true engine for organizational growth and efficiency. Get ready to build a knowledge management framework that works.
1. Visual Process Documentation with Screenshots and Callouts
Text-only documentation often fails to capture the nuances of digital workflows, leaving team members confused and processes prone to error. One of the best knowledge management practices to combat this is visual process documentation. This method uses annotated screenshots and visual callouts to transform complex procedures into clear, step-by-step visual guides. By showing exactly where to click, what to type, and which buttons to press, this approach dramatically reduces cognitive load and improves comprehension.
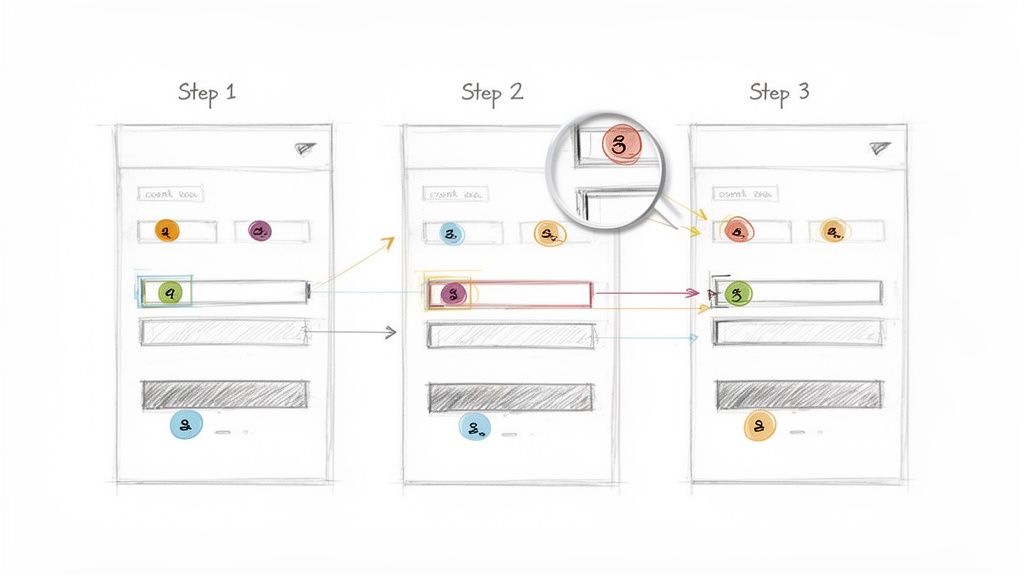
This practice is essential for any process that takes place within a software interface. It ensures that instructions are not just read but seen, making them immediately actionable and minimizing the need for follow-up questions. It’s a foundational technique for building a reliable and scalable knowledge base.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Visual documentation is effective because it mirrors how users actually interact with technology. Instead of translating a visual interface into abstract text, it presents the process in its native context. This is particularly valuable for customer support teams creating help articles, product teams guiding users through new features, and operations managers standardizing internal software usage. For example, a support agent can resolve a ticket much faster by following an annotated screenshot than by deciphering a dense paragraph of instructions.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Automate Capture: Use tools like Build a Guide or Snagit to automate the screenshot capture process. This maintains consistency and saves significant time, especially for multi-step workflows. Build a Guide even uses AI to auto-generate annotations and descriptions.
Establish a Visual Style Guide: Create and enforce a consistent style for callouts, arrows, and highlights. Use specific colors to denote actions (e.g., red for a required click, blue for optional information) across all your guides.
Provide Context: Include both zoomed-in screenshots focusing on a specific element and full-screen captures that show where that element is located on the page.
Maintain with UI Updates: Visual guides become obsolete the moment an interface changes. Implement a process to review and update screenshots immediately after every software update to prevent confusion and maintain trust in your knowledge base.
2. Interactive Step-by-Step Guides with Progressive Disclosure
Static documents can overwhelm users with too much information at once, leading to confusion and abandonment. A more effective knowledge management practice is the use of interactive step-by-step guides. This method breaks down complex processes into a sequence of small, manageable actions. It uses the principle of progressive disclosure to reveal information only when it is needed, preventing cognitive overload and guiding the user through the workflow one step at a time.
This approach transforms passive reading into an active, engaging experience. By focusing the user on a single task at a time, it significantly improves completion rates and reduces errors. This makes it an ideal solution for employee onboarding, customer training, and guiding users through multi-stage tasks like setting up a new software integration.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Interactive guides are powerful because they align with how people learn and execute tasks most effectively: sequentially and with focus. Instead of forcing a user to mentally map a long list of text instructions to a live interface, the guide walks them through it in real-time. This is invaluable for customer success teams aiming to boost feature adoption, operations managers standardizing complex internal procedures, and product teams looking to improve the user onboarding experience, similar to the guided tours seen in products like Intercom or HubSpot.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Keep Each Step Singular: Design each step to address one primary action. For example, a single step should be "Click the 'Save' button," not "Fill out the form, select your preferences, and then click 'Save'."
Provide "Why" Context: Briefly explain the purpose of a step before asking the user to complete it. This builds understanding and makes the process feel less robotic.
Allow for Skips: Enable users to skip steps they have already completed or that are irrelevant to their specific needs. This respects their existing knowledge and saves time.
Test the Flow: Before publishing, have a member of your target audience run through the guide to identify confusing steps or awkward sequencing. Tools like Build a Guide help create these guided experiences with ease. For more details on this methodology, you can learn how to create an effective step-by-step guide.
3. Collaborative Documentation and Real-Time Co-Editing
Static, single-owner documents quickly become knowledge silos, trapping valuable insights with one person and creating bottlenecks for updates. One of the best knowledge management practices to dismantle these silos is collaborative documentation with real-time co-editing. This approach enables multiple team members to create, edit, and refine knowledge assets simultaneously, transforming documentation from a solo task into a dynamic, team-owned resource. By democratizing the creation process, organizations can leverage subject matter experts from different departments to build more comprehensive and accurate guides.
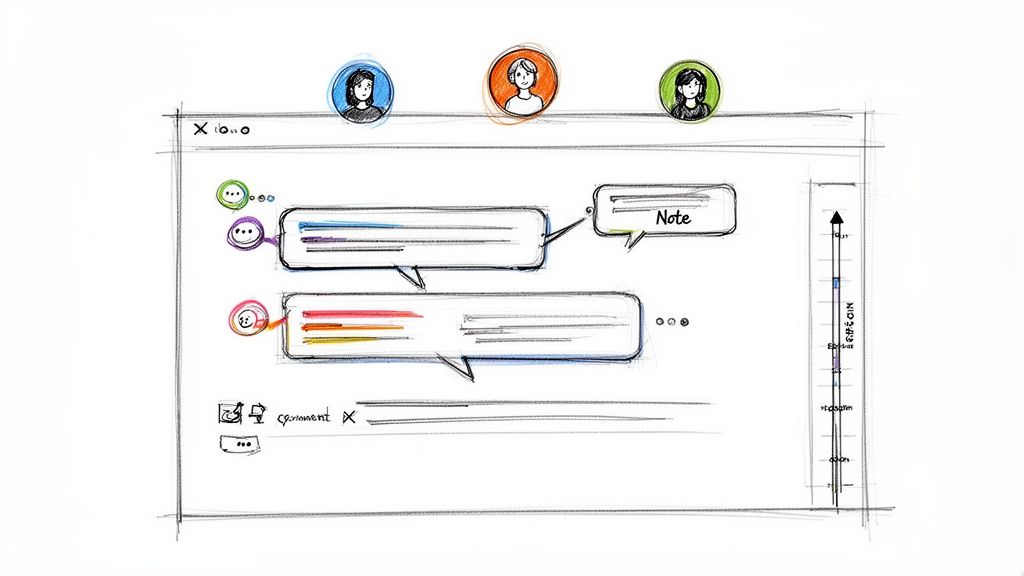
This method ensures knowledge stays current through continuous, collective improvement rather than sporadic, top-down updates. Platforms like Google Workspace, Notion, and Confluence pioneered this real-time model, allowing distributed teams to work together as if they were in the same room, building a single source of truth that evolves with the organization.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Collaborative documentation accelerates knowledge capture and improves its quality by incorporating diverse perspectives in real time. Instead of a linear review process that can take days, feedback and edits happen concurrently, leading to faster creation cycles. This is particularly crucial for product teams developing feature guides, operations managers creating cross-departmental SOPs, and support teams building a shared knowledge base. For truly collaborative documentation, mastering the art of taking minutes of meeting is essential to transform discussions into actionable knowledge and shared records. This ensures that valuable conversations are not lost but are instead integrated directly into the living documents that guide the team.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Establish Clear Standards: Before opening a document for collaboration, define a style guide covering formatting, tone, and structure. This prevents inconsistencies when multiple authors contribute.
Assign a Documentation Owner: Designate a single person as the "owner" or final editor for each key document. Their role is not to write everything but to ensure quality, consistency, and final approval.
Leverage Commenting for Feedback: Encourage team members to use commenting features for suggestions and questions rather than making direct, unapproved edits. This maintains the integrity of the original text while fostering discussion.
Create a Review Workflow: Implement a simple workflow with clear approval gates. For instance, a draft is created collaboratively, then moves to a subject matter expert for review, and finally to the owner for publishing.
Document the Process Itself: Create a guide on how to contribute to your knowledge base. This "meta-document" should outline the standards, tools, and workflows for new contributors to follow.
4. Audience-Specific Knowledge Segmentation and Personalization
Creating one-size-fits-all documentation often leads to information that is too generic for experts and too complex for beginners. One of the best knowledge management practices to solve this is audience-specific knowledge segmentation. This strategy involves tailoring content to specific user roles, skill levels, and goals, ensuring that everyone from a new customer to a power user or internal support agent gets precisely the information they need.
This practice moves beyond a single, monolithic knowledge base to a more dynamic, personalized resource. By segmenting content, you dramatically increase its relevance and usability, which boosts adoption and reduces the cognitive load required to find answers. It's the difference between handing someone a phone book and giving them a direct phone number.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Audience-specific documentation is effective because it acknowledges that different users have different needs. A new employee in HR requires a different onboarding guide than a seasoned developer, and a customer using a basic feature needs different support than one using an advanced API. Companies like Salesforce and HubSpot excel at this by creating separate help portals for administrators, developers, and end-users, ensuring each group finds relevant guidance quickly.
This approach is crucial for customer success teams aiming to reduce support tickets and for product teams trying to improve feature adoption. When users feel the documentation speaks directly to their problems, they are more likely to self-serve and engage more deeply with the product or process.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Define User Personas: Start by creating clear definitions for your key audience segments (e.g., "New Customer," "Project Manager," "Support Agent"). Survey users to understand their specific roles, goals, and common pain points.
Tag Content for Filtering: Use a robust tagging system within your knowledge base. Apply audience-specific tags (like
role:managerorskill-level:beginner) to every article, allowing users to easily filter for relevant content.Create Role-Based Learning Paths: Group segmented content into logical learning paths or collections. For example, create a "Manager Onboarding" collection that guides a new leader through all necessary processes and tools.
Use Progressive Disclosure: For beginner-focused guides, hide advanced options or technical details behind expandable "Learn More" sections. This keeps the initial view clean and simple while still providing depth for those who need it.
5. Engagement Analytics and Knowledge Effectiveness Tracking
Creating knowledge is only half the battle; understanding if it's actually being used and if it's effective is what separates a good knowledge base from a great one. This is where Engagement Analytics and Knowledge Effectiveness Tracking becomes an indispensable practice. This data-driven approach measures how users interact with documentation through metrics like view counts, completion rates, time spent on a guide, and user engagement hotspots. Analytics transform your knowledge base from a static content library into a dynamic, continuously optimized resource.
This practice is critical for any team that relies on documentation to drive outcomes, such as reducing support tickets or speeding up employee onboarding. By analyzing user behavior, you can pinpoint exactly where users struggle, which articles are most valuable, and what content needs to be updated or clarified. It’s a foundational technique for proving the ROI of your knowledge management efforts.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Tracking knowledge effectiveness moves you from assumptions to evidence-based improvements. Instead of guessing which guides are helpful, you can see precisely which ones are viewed most often, which have the highest completion rates, and where users drop off. This is invaluable for customer support teams aiming to reduce ticket volume by improving help articles, and for operations managers seeking to streamline internal training. For instance, if an onboarding guide has a 90% drop-off rate on step three, you have a clear signal that the step is confusing and needs immediate attention.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Set Baselines: Before updating a key process guide, capture baseline metrics for views, completion rates, and time spent. Use this data to measure the impact of your changes.
Identify Drop-Off Points: Use tools with step-by-step analytics, like Build a Guide, to monitor completion rates for each part of a workflow. A significant drop-off indicates a point of friction that needs to be simplified or clarified.
Correlate with Business Outcomes: Connect your knowledge base analytics to key business metrics. Track whether views on a specific troubleshooting guide correlate with a reduction in related support tickets, or if high engagement on onboarding materials leads to faster ramp-up times.
Create Health Dashboards: Develop a simple monthly or quarterly dashboard to review the health of your documentation. Highlight top-performing articles, underutilized content, and guides with poor engagement metrics to prioritize maintenance efforts.
6. Living Documentation with Version Control and Automatic Updates
One of the biggest threats to a knowledge base is obsolescence. Static documents quickly become outdated, creating distrust and process errors. The solution is to treat your documentation as a living, evolving asset integrated directly with your workflows. This practice ensures that as your processes, products, or software change, your documentation updates in tandem, often automatically. It’s a dynamic approach that prevents the "stale documentation" problem plaguing many organizations.
By connecting documentation to version control systems like Git or using modern tools with built-in update triggers, this method transforms knowledge management from a manual chore into a reliable, self-maintaining system. It is one of the best knowledge management practices for fast-moving companies where accuracy is non-negotiable.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Living documentation eliminates the gap between a process and its guide. For development teams, this means API documentation, like Stripe's, automatically reflects the latest code changes. For operations teams, a change in a core business application can trigger an immediate update to the corresponding standard operating procedure (SOP). This real-time synchronization builds immense trust in your knowledge base, as users know the information is always current and reliable. It’s particularly critical for distributed teams that depend entirely on documented processes to stay aligned.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Establish Automatic Triggers: Connect your documentation platform to your source of truth. For instance, integrate your knowledge base with your code repository (using tools like GitBook) so a code merge prompts a documentation review. For business processes, use tools like Build a Guide which can detect UI changes and prompt creators to update affected visual guides.
Implement a Review Workflow: Automation should not mean a lack of oversight. Implement a mandatory peer-review or approval step before any automated update goes live to ensure quality and clarity.
Maintain a Visible Change Log: Transparency is key. Provide users with an accessible version history or change log for each document. This allows them to see what changed, when, and why, which is crucial for auditing and training purposes.
Set Up Staleness Alerts: Create automated alerts that notify document owners when a guide hasn't been reviewed or updated in a set period (e.g., 90 days). This proactive measure helps catch outdated information before it becomes a problem.
7. Searchable Knowledge Bases with Intelligent Information Architecture
Creating documentation is only half the battle; ensuring team members and customers can find it is what makes it valuable. One of the best knowledge management practices is to build a searchable knowledge base with intelligent information architecture. This approach organizes content using an intuitive taxonomy, clear hierarchies, and powerful search functionality. Instead of burying answers in lengthy documents, it structures content for maximum discoverability through logical categorization and tagging.
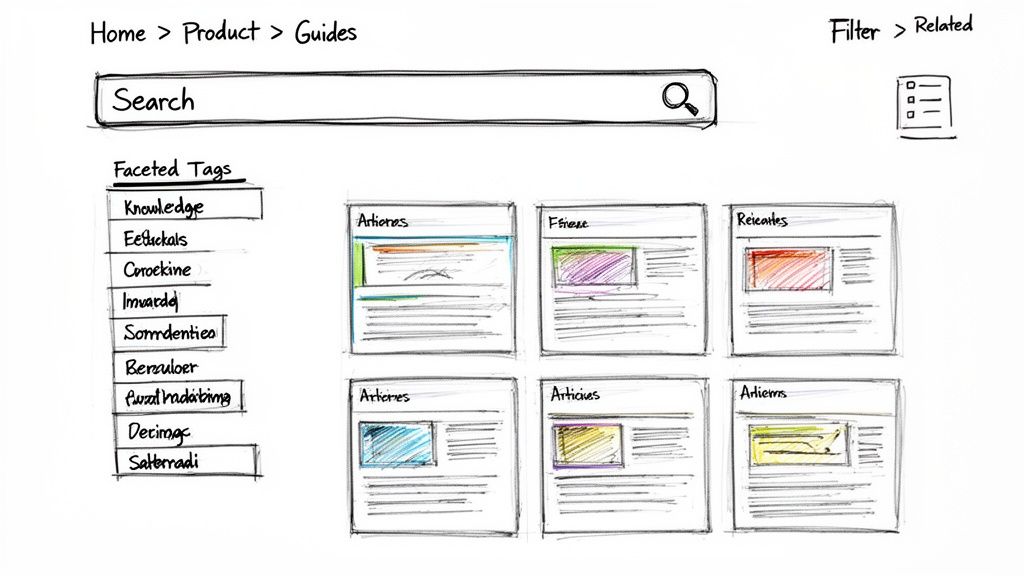
This practice ensures users can find answers through browsing or searching with equal ease, reducing frustration and resolution time. It’s the difference between a digital library and a digital junk drawer. Companies like Zendesk and HubSpot excel at this, creating help centers where finding information feels effortless.
Why It’s a Top Practice
An intelligent information architecture directly impacts user autonomy and operational efficiency. For customer support teams, it means fewer repetitive tickets as customers find their own answers. For internal teams, it reduces the time employees spend searching for information and asking colleagues for help. This structured approach makes knowledge scalable, preventing it from becoming an unmanageable mess as your organization grows. Beyond traditional search functionalities, advanced knowledge bases can further enhance information retrieval by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to understand context and intent.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Use User Language: Build your taxonomy with terms your users actually search for, not internal jargon. Analyze support tickets and search queries to understand their vocabulary.
Keep Hierarchies Flat: Create clear, high-level categories with minimal nesting. Aim for a structure that is no more than two or three levels deep to prevent users from getting lost.
Tag Content Extensively: Apply multiple relevant tags and keywords to each article. This aids discovery through faceted search and accommodates different search terms for the same concept.
Analyze Search Analytics: Regularly review your knowledge base's search analytics to identify what users are looking for but can't find. Use these content gaps to prioritize what to create next.
Create Topic-Based Landing Pages: For major products or use cases, build dedicated landing pages that group all relevant articles, guides, and FAQs in one place. If you're looking for guidance, see this detailed guide on how to build a knowledge base from the ground up.
8. Embedded Contextual Help and Just-In-Time Learning
Forcing users to abandon their workflow to search a separate knowledge base is a major source of friction and frustration. An exceptional knowledge management practice is embedded contextual help, which delivers guidance exactly when and where users need it. This just-in-time learning approach integrates support directly into the user interface through tooltips, guided tours, and contextual sidebars that address immediate challenges. By providing answers within the task environment, you dramatically improve user adoption and task completion rates.
This practice is critical for onboarding new users to software, guiding them through complex features, or providing support without disrupting their focus. It shifts knowledge from a destination to be sought out into a seamless part of the user experience, making learning feel intuitive and effortless.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Embedded contextual help is powerful because it addresses user needs at the moment of friction, significantly reducing cognitive load. Instead of making users remember complex instructions from an external article, it provides bite-sized, relevant information in their immediate view. This is invaluable for product teams aiming to boost feature adoption, as seen with Salesforce's in-app guidance, and for support teams looking to proactively deflect tickets, like Zendesk’s help widget. The information is delivered at the point of need, which is proven to increase retention and reduce user error.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Trigger Help Based on Behavior: Use tools like Intercom or Pendo to launch contextual help based on user actions, such as hesitating on a form field or visiting a new feature page for the first time. This ensures the guidance is relevant and not just random noise.
Keep Guidance Brief and Actionable: Contextual messages should be concise. Aim for under 100 words and focus on a single, clear action the user can take immediately.
Allow Easy Dismissal: Ensure users can easily close or hide any in-app help. A persistent, un-closable pop-up creates a negative experience and defeats the purpose of being helpful.
Use Progressive Disclosure: For complex features, reveal information in layers. Start with a simple tooltip and offer a link to a more detailed guide or tour for users who want to learn more.
Measure Effectiveness: Track how users interact with your embedded help. Monitor metrics like dismissal rates, completion rates for guided tours, and whether viewing a help widget correlates with successful task completion. Use this data to refine your messages.
9. Centralized SOP Library with Multi-Channel Publishing
Maintaining separate documentation for different platforms is a recipe for inconsistency and outdated information. A far superior approach is to create a centralized SOP library with multi-channel publishing. This knowledge management practice involves establishing a single source of truth for all standard operating procedures and then using automation to distribute that content to various channels, such as branded help centers, internal wikis, and customer portals. This "create once, publish everywhere" model ensures that every team member and customer sees the same, most current information, regardless of where they access it.
This practice is critical for organizations that serve diverse audiences across multiple touchpoints. It eliminates the tedious and error-prone task of manually updating documents in several locations, guaranteeing that your knowledge base remains a reliable and unified resource. By decoupling content creation from its presentation, teams can focus on quality while the system handles consistent delivery.
Why It’s a Top Practice
A centralized library with multi-channel publishing directly combats content fragmentation, a common failure point in knowledge management. When documentation lives in disparate systems, it inevitably diverges, creating confusion and eroding trust. This practice is particularly valuable for product teams that need to supply documentation for both internal support agents and external users, or for agencies that deliver standardized processes to multiple clients, each with their own branded portal. For instance, AWS successfully uses this model to publish its extensive documentation across its website, developer portals, and offline formats, all from a single source.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Map Your Channels: Begin by identifying every location where your documentation is currently published or needs to be. This includes your intranet, customer help desk, public-facing knowledge base, and even PDF exports.
Standardize with Templates: Create standardized templates for your SOPs within your central repository. This ensures that when the content is published, it adapts correctly to the formatting requirements of each channel.
Automate Publishing Workflows: Use tools like Build a Guide or GitBook that are designed for multi-channel output. Set up automated pipelines that trigger updates across all connected channels whenever a change is made to the source document.
Implement Version Control at the Source: Treat your central library as the definitive record. Implement robust version control to track changes, review histories, and manage updates methodically before they are pushed live to all channels.
10. Knowledge Governance and Continuous Improvement Workflows
A knowledge base without oversight quickly becomes a digital junkyard of outdated, inaccurate, and irrelevant information. One of the most critical knowledge management practices is establishing knowledge governance and continuous improvement workflows. This practice institutes clear ownership, review processes, and feedback loops to ensure documentation quality, accuracy, and relevance over time. By defining who is responsible for what, it transforms documentation from a one-time task into a living, evolving asset.

This practice is essential for preventing knowledge decay and maintaining user trust. It ensures that when a team member finds a guide or policy, they can be confident it is the correct, up-to-date version. For distributed teams and growing SMBs, strong governance is the backbone of a scalable and reliable knowledge management system.
Why It’s a Top Practice
Knowledge governance is effective because it embeds accountability and quality control directly into your documentation lifecycle. Instead of a free-for-all where anyone can publish anything, it creates a structured system that upholds standards. This is invaluable for operations and HR teams standardizing onboarding processes, as well as for agencies delivering reliable SOPs to clients. For example, Red Hat’s well-defined documentation review cycles ensure their complex technical guides remain trustworthy for a global user base.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Assign Clear Owners: Assign a specific owner or team to every major section or category of your knowledge base. They are the designated point of contact for updates and questions.
Implement Simple Approval Workflows: Create a straightforward review process before new documentation is published. This could be a simple peer review or a manager's sign-off; avoid overcomplicating it.
Schedule Regular Review Cycles: Set automated reminders for content owners to review their documentation quarterly or biannually. Use alerts to flag content that hasn't been updated in over six months.
Integrate User Feedback: Add a simple "Was this helpful?" button or a feedback form at the end of each article to collect direct input from users.
Make Improvement a Team Responsibility: While owners are accountable, foster a culture where everyone feels empowered to suggest edits and improvements. To learn more about building these systems, explore these process improvement best practices.
Top 10 Knowledge Management Practices Comparison
Approach | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource & Maintenance ⚡ | Expected Effectiveness ⭐ | Primary Impact 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Visual Process Documentation with Screenshots and Callouts | 🔄 Medium — manual capture and frequent updates required | ⚡ Moderate — designers/SMEs, image storage & optimization | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — high comprehension for UI tasks | 📊 Lowers support tickets; faster task completion | 💡 SaaS onboarding, UI walkthroughs, user-facing help |
Interactive Step-by-Step Guides with Progressive Disclosure | 🔄 Medium — flow design, conditional branching | ⚡ Moderate — UX dev and content sequencing | ⭐⭐⭐ — improves completion and reduces overwhelm | 📊 Higher completion rates; guided feature adoption | 💡 Onboarding, complex setups, troubleshooting wizards |
Collaborative Documentation and Real-Time Co-Editing | 🔄 Low–Medium — tool setup + governance | ⚡ Low–Moderate — collaboration tools, editors | ⭐⭐⭐ — better accuracy via peer contributions | 📊 Faster doc creation; reduces knowledge silos | 💡 Distributed teams, cross-functional knowledge capture |
Audience-Specific Knowledge Segmentation and Personalization | 🔄 High — multiple variants and routing logic | ⚡ High — more content, tagging, personalization rules | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — higher relevance and engagement | 📊 Increased adoption; reduced role-based confusion | 💡 SaaS with diverse personas; customer success teams |
Engagement Analytics and Knowledge Effectiveness Tracking | 🔄 Medium — instrumentation and analysis workflows | ⚡ Moderate–High — analytics tools + analysts | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — enables data-driven improvements | 📊 Identifies gaps; prioritizes content updates (ROI) | 💡 Ops, success teams, large KB performance monitoring |
Living Documentation with Version Control & Automatic Updates | 🔄 High — system integrations and automation | ⚡ High — engineering, CI/CD pipelines, governance | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — keeps docs current; reduces stale content | 📊 Ensures accuracy, audit trails, fast rollbacks | 💡 API docs, dev-centric products, compliance-heavy orgs |
Searchable Knowledge Bases with Intelligent IA | 🔄 Medium — taxonomy and search tuning | ⚡ Moderate — content modeling and search tech | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — faster findability and self-service | 📊 Reduces time-to-answer; lowers common tickets | 💡 Support centers, extensive documentation libraries |
Embedded Contextual Help and Just‑In‑Time Learning | 🔄 Medium–High — in‑product integration & timing rules | ⚡ Moderate — product dev + UX/content coordination | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — improves retention and feature use | 📊 Reduces context switching; increases adoption | 💡 In-app onboarding, task-specific guidance, complex UIs |
Centralized SOP Library with Multi‑Channel Publishing | 🔄 High — consolidation, templates, publishing pipelines | ⚡ High — migration effort, publishing automation | ⭐⭐⭐ — consistent cross-channel information | 📊 Eliminates duplicate versions; simplifies maintenance | 💡 Organizations publishing to web, mobile, PDF, portals |
Knowledge Governance & Continuous Improvement Workflows | 🔄 High — ownership, SLAs, review cycles | ⚡ Moderate — people, workflows, enforcement | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — sustains quality and accuracy over time | 📊 Prevents neglect; drives continuous doc improvements | 💡 Regulated industries, large enterprises, agencies |
From Theory to Action: Building Your Knowledge-Driven Culture
You've explored the ten pillars of modern, effective knowledge management, from the granular detail of visual process documentation to the high-level strategy of robust governance. The journey from scattered information to a centralized, living knowledge base can seem daunting, but it's a strategic imperative for any growing business, especially distributed teams, agencies, and customer-facing departments. The core theme connecting all these practices is a fundamental shift in perspective: knowledge is not a static document to be filed away, but a dynamic, operational asset that fuels efficiency, consistency, and growth.
Implementing these best knowledge management practices is less about a one-time project and more about cultivating a continuous cycle of improvement. It’s about creating an environment where capturing a workflow is as natural as sending an email, and finding an answer is faster than asking a colleague. This cultural shift is the true engine of a knowledge-driven organization.
Synthesizing the Core Principles
Let's distill the key takeaways from the practices we've covered. True knowledge management excellence isn't achieved by tackling just one area; it's the synergistic effect of combining several strategic approaches.
Make it Engaging and Accessible: Practices like Visual Process Documentation and Interactive Step-by-Step Guides transform learning from a passive chore into an active experience. When information is easy to consume and immediately applicable, adoption rates soar.
Make it Collaborative and Alive: The era of the lone document author is over. Collaborative Documentation and Living Documentation with Version Control ensure your knowledge base is a dynamic reflection of your current processes, not an outdated archive.
Make it Intelligent and Contextual: Don’t force users to hunt for information. Searchable Knowledge Bases, Audience-Specific Segmentation, and Embedded Contextual Help bring the right answers to the right people at the exact moment of need.
Make it Governed and Measurable: Without structure, even the best content descends into chaos. Knowledge Governance provides the framework for quality, while Engagement Analytics offers the data to prove ROI and identify areas for improvement.
Your Actionable Roadmap to a Knowledge-Driven Future
Moving from theory to implementation requires a deliberate, focused approach. You don't need to boil the ocean. Instead, start with a single, high-impact area and build momentum.
Identify a Critical Knowledge Gap: Where is tribal knowledge causing the most friction? Is it in onboarding a new customer success manager? Standardizing a client deliverable process for your agency? Documenting a complex internal software workflow? Pinpoint one process that, if standardized, would deliver immediate value.
Choose Two or Three Practices to Apply: Start small. For that identified process, commit to applying a few of the best knowledge management practices discussed. For example, you could combine Visual Process Documentation (#1) with an Interactive Step-by-Step Guide (#2) and publish it to a Centralized SOP Library (#9).
Empower a Champion: Designate a process owner or a small team to lead the initial effort. This champion will set the standard, gather feedback, and demonstrate the value of this new approach to the rest of the organization.
Measure and Evangelize: Track the impact. Did it reduce support ticket volume? Did it cut onboarding time for a specific role? Use the data from Engagement Analytics (#5) to build a business case and evangelize the success. This creates a powerful feedback loop that encourages broader adoption.
Ultimately, the goal is to build an operational nervous system for your business-a single source of truth that empowers team members, delights customers, and creates a foundation for scalable, consistent execution. By thoughtfully implementing these best knowledge management practices, you are not just organizing documents; you are future-proofing your organization’s most valuable asset: its collective intelligence.
Ready to turn your complex processes into simple, interactive guides automatically? Build a Guide helps you implement many of these best practices by instantly converting screen recordings into beautiful, step-by-step documentation you can share anywhere. Start building your single source of truth today at Build a Guide.

